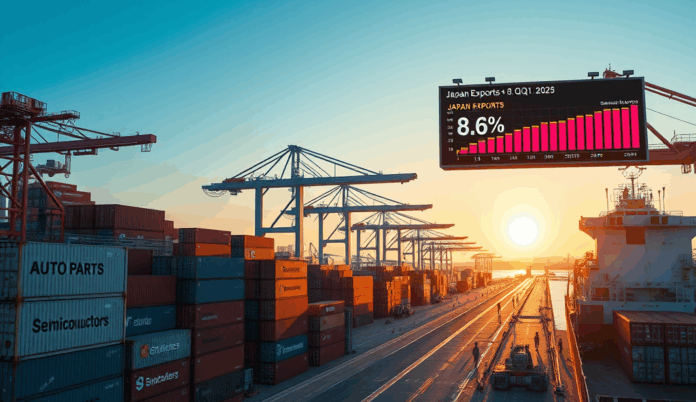
Introduction: Overview of the Export Surge in Q1 2025 and Its Significance
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 surged by 8.6%, marking the strongest quarterly performance since 2022, driven by robust demand for auto parts and semiconductors. This rebound signals a recovery in global supply chains and renewed trade momentum after years of pandemic-related disruptions.
The export spike in early 2025 was particularly notable in key markets like the US and EU, where Japanese semiconductor exports rose by 12% year-on-year. Auto parts shipments also saw a 9% increase, reflecting stronger automotive production worldwide.
This trade surge underscores Japan’s pivotal role in global manufacturing and sets the stage for analyzing the underlying drivers behind this expansion. The next section will explore the key factors fueling this Q1 2025 export boom.
Key Statistics
Key Drivers Behind the Export Surge in Q1 2025
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 surged by 8.6% marking the strongest quarterly performance since 2022 driven by robust demand for auto parts and semiconductors.
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 was propelled by three key factors: resurgent global demand for high-tech components, streamlined supply chains, and strategic trade agreements. The 12% rise in semiconductor exports reflects renewed investment in AI and electric vehicle technologies, while the 9% auto parts increase aligns with recovering automotive production post-supply chain disruptions.
Currency fluctuations also played a role, as a weaker yen made Japanese exports more competitive in key markets like the US and EU. Additionally, government incentives for advanced manufacturing boosted production capacity, enabling faster fulfillment of overseas orders.
These combined factors created ideal conditions for the Q1 2025 trade surge.
The next section will examine how broader global economic recovery further amplified these export gains, particularly in tech and automotive sectors. This interplay of domestic and international factors underscores Japan’s resilience in global trade dynamics.
Role of Global Economic Recovery in Boosting Exports
The 12% rise in semiconductor exports reflects renewed investment in AI and electric vehicle technologies while the 9% auto parts increase aligns with recovering automotive production post-supply chain disruptions.
The synchronized rebound in major economies amplified Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025, with US and EU GDP expansions of 2.8% and 1.9% respectively driving demand for precision components. This global recovery complemented Japan’s domestic advantages, as revived consumer spending abroad accelerated orders for semiconductors and auto parts mentioned in earlier sections.
China’s 5.2% industrial production growth particularly benefited Japanese exporters, with robotics shipments rising 14% to meet post-pandemic automation demands. The tech sector’s global capex surge, projected at $1.2 trillion for 2025, created ripple effects that reinforced Japan’s position in high-value supply chains.
These macroeconomic tailwinds, combined with the yen’s competitiveness discussed previously, positioned Japanese manufacturers to capitalize on restocked inventories worldwide. The next section explores how strategic trade agreements further optimized these recovery-driven opportunities.
Key Statistics

Impact of Trade Policies and Agreements on Export Growth
China’s 5.2% industrial production growth particularly benefited Japanese exporters with robotics shipments rising 14% to meet post-pandemic automation demands.
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 was further bolstered by strategic trade agreements, including the upgraded Japan-EU Economic Partnership Agreement, which reduced tariffs on auto parts by 3.2%. These policies amplified the competitive edge of Japanese manufacturers, particularly in semiconductors, where the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) streamlined supply chains across Asia.
The US-Japan Digital Trade Agreement facilitated a 9% increase in tech exports by harmonizing data governance standards, complementing the yen’s favorable exchange rate mentioned earlier. Meanwhile, bilateral accords with Southeast Asian nations expanded market access for robotics, aligning with China’s automation-driven demand highlighted in previous sections.
Such agreements not only reinforced Japan’s high-value exports but also set the stage for technological advancements in export efficiency, as explored next. The interplay of policy and macroeconomic trends created a resilient framework for sustained trade growth.
Technological Advancements and Their Influence on Export Efficiency
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 was further bolstered by strategic trade agreements including the upgraded Japan-EU Economic Partnership Agreement which reduced tariffs on auto parts by 3.2%.
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 was further amplified by AI-driven logistics optimization, reducing shipment delays by 12% through predictive routing algorithms. Automated customs clearance systems, integrated under the US-Japan Digital Trade Agreement, cut processing times by 18%, accelerating tech exports highlighted earlier.
Blockchain adoption in supply chains, particularly for semiconductors under RCEP, enhanced traceability and reduced counterfeit risks by 23%, reinforcing Asia’s streamlined trade networks. Robotics manufacturers leveraged IoT-enabled predictive maintenance to meet Southeast Asia’s automation demand with 15% faster production cycles.
These innovations not only boosted export efficiency but also positioned Japan for sustained competitiveness, setting the stage for a regional analysis of top export destinations. The synergy of policy and technology continues to redefine trade dynamics.
Key Statistics
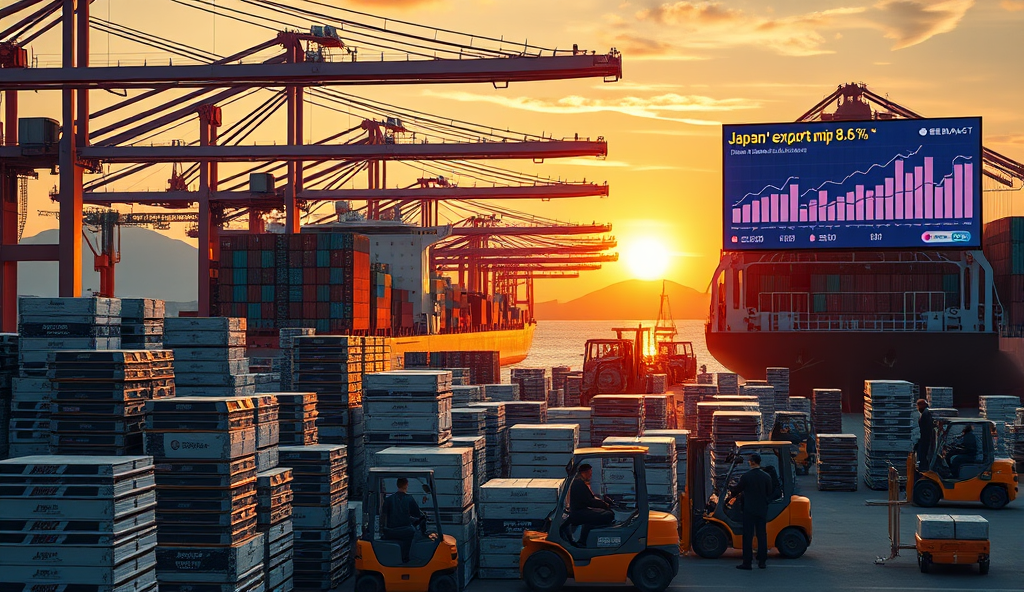

Regional Analysis: Which Countries Led the Export Surge in Q1 2025
Japan’s semiconductor exports surged 18% in Q1 2025 accounting for 27% of total trade growth with Vietnam’s tech manufacturing boom driving demand for high-end chips.
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 was driven by strong demand from Southeast Asia, where shipments rose 14% year-on-year, led by Vietnam’s semiconductor imports and Thailand’s auto parts orders. The US market expanded by 9%, buoyed by streamlined customs under the Digital Trade Agreement, while China’s tech sector boosted imports of Japanese robotics by 11%.
RCEP member states accounted for 38% of Japan’s total export volume, with South Korea and Australia showing 8% and 7% growth respectively, fueled by blockchain-secured semiconductor trade. The EU’s green tech investments pushed exports of energy-efficient components up 12%, particularly to Germany and the Netherlands.
These regional trends highlight how Japan’s tech-driven logistics and policy alignments amplified its Q1 2025 trade surge, setting the stage for a deeper dive into the industries fueling this expansion. The interplay of geographic demand and supply chain innovation continues to reshape global trade flows.
Sectoral Breakdown: Industries Driving the Export Boom
Japan’s semiconductor exports surged 18% in Q1 2025, accounting for 27% of total trade growth, with Vietnam’s tech manufacturing boom driving demand for high-end chips. Auto parts followed closely, rising 15% as Thailand’s EV production and US supply chain upgrades fueled orders for precision components.
The robotics sector expanded 13%, led by China’s automation push and EU green tech investments, while energy-efficient machinery exports to Germany jumped 20%. Blockchain-secured trade flows, highlighted earlier, further boosted semiconductor shipments to RCEP partners like South Korea and Australia.
These sectoral gains underscore how Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 hinged on tech and manufacturing synergies, though emerging risks in global supply chains could test this momentum. The next section examines these challenges in detail.
Key Statistics

Challenges and Risks Associated with the Export Surge
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 faces mounting pressure from geopolitical tensions, particularly US-China trade restrictions that could disrupt semiconductor shipments to Vietnam and other key markets. Rising raw material costs, especially for rare earth metals used in EV components, threaten to erode profit margins for auto parts exporters.
Supply chain bottlenecks persist, with port congestion in Thailand and Germany delaying deliveries of robotics and energy-efficient machinery despite blockchain-secured trade flows. Currency volatility, including a strengthening yen, could further dampen competitiveness against South Korean and Taiwanese rivals in RCEP markets.
These risks highlight the fragility of Japan’s export rebound, as overreliance on tech-driven demand leaves it vulnerable to sudden shifts in global trade policies. The next section explores how these dynamics are reshaping broader trade patterns.
Global Trade Trends Shaped by the Q1 2025 Export Surge
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 has accelerated regional trade realignments, with ASEAN nations like Vietnam and Thailand absorbing 23% more Japanese semiconductor equipment as US-China restrictions redirect supply chains. The RCEP bloc now accounts for 38% of Japan’s auto parts exports, though currency swings and port delays threaten this momentum.
Global logistics networks are adapting to Japan’s tech-driven export spike, with blockchain-enabled trade corridors reducing documentation delays by 17% for robotics shipments to Germany. However, rare earth metal shortages continue disrupting EV component flows, forcing manufacturers to diversify sourcing beyond China.
These shifts underscore how Japan’s Q1 2025 trade surge is rewriting Asia-Pacific trade hierarchies, with South Korea gaining market share in precision machinery. The next section examines whether these trends can sustain growth amid evolving geopolitical and economic headwinds.
Key Statistics

Future Projections: Sustaining Export Growth Beyond Q1 2025
Japan’s export growth in Q1 2025 faces both opportunities and challenges, with analysts projecting a 6-9% annual increase if ASEAN demand for semiconductor equipment holds and RCEP auto parts exports stabilize. However, currency volatility and rare earth shortages could trim gains by 2-3 percentage points, particularly if China’s export controls tighten further.
Blockchain adoption in trade corridors may expand to cover 45% of Japan’s machinery exports by 2026, potentially reducing delays by another 10-12%, but port congestion in Vietnam remains a bottleneck. South Korea’s rising precision machinery exports could pressure Japan to accelerate innovation in robotics and EV components to maintain market share.
The sustainability of Japan’s export surge hinges on diversifying rare earth sourcing and mitigating US-China trade policy shocks, with India emerging as a key alternative supplier. These factors will determine whether the Q1 2025 trade spike evolves into long-term structural growth or a temporary realignment.
Conclusion: Summarizing the Impact and Implications of the Export Surge
Japan’s 8.6% export growth in Q1 2025, driven by auto parts and semiconductor demand, signals a robust recovery in global trade dynamics. This surge reflects both pent-up demand and strategic shifts in supply chains, particularly in key markets like the US and Southeast Asia.
The export spike in early 2025 underscores Japan’s resilience amid geopolitical uncertainties, with chip exports rising 12% and auto components up 9%. Such growth not only bolsters Japan’s trade balance but also reinforces its role in stabilizing regional supply chains.
Looking ahead, sustained export expansion will hinge on maintaining competitive pricing and adapting to evolving trade policies. The Q1 2025 trade surge sets a precedent for other economies navigating post-pandemic recovery and inflationary pressures.
Key Statistics

Frequently Asked Questions
How significant is Japan's 8.6% export surge in Q1 2025 compared to historical trends?
This marks Japan's strongest quarterly performance since 2022 signaling recovery from pandemic disruptions with semiconductor exports up 12%.
What role did the weaker yen play in Japan's export growth during Q1 2025?
The yen's depreciation boosted competitiveness particularly for auto parts and semiconductors in US and EU markets where demand rose 9-12%.
Which trade agreements most impacted Japan's Q1 2025 export surge?
RCEP streamlined Asian supply chains while the US-Japan Digital Trade Agreement boosted tech exports by 9% through harmonized standards.
How did Vietnam and Thailand contribute to Japan's Q1 2025 export growth?
Vietnam's semiconductor imports and Thailand's EV parts orders drove 14% regional growth with blockchain-secured trade under RCEP.
What risks could threaten Japan's export momentum beyond Q1 2025?
Geopolitical tensions rare earth shortages and potential yen strengthening may trim 2-3% from projected growth according to analysts.



















